Water: a source of life and (renewable) energy

Image taken from http://planete-energies.com
Can you guess what is the most important component of life? Have you guessed it already?
You are right, it is water, which is everywhere! The fact about water is that it is always moving, rivers and waterfalls are a great example of moving water. People are using this movement to create power, and this is called hydropower.
What is hydropower?
Hydropower is a clean, renewable and reliable energy source which converts kinetic energy from falling water into electricity, without consuming more water than is produced by nature.
It is quite simply the oldest method by which renewable energy has been harnessed by the human race. The first water wheels were used well over 2000 years ago, and the technology has since been refined to become very efficient in the production of electricity.
Hydroelectricity is electricity which is made by the movement of water. It is usually generated with dams that block rivers to make a reservoir or collect water that it pumped there. When the water is "released", the huge pressure behind the dam forces the water down the pipes ("penstock") which lead to a turbine. This causes the turbine to turn, leading to production of electricity by the generator. Most of hydropower is generated this way! The power extracted from the water depends on the volume and on the heigh difference between the source and the water outlow.
Using dams to produce hydropower is more environmentally-friendly than steam engines. In fact, some places like Norway and Quebec get most of their electricity this way!
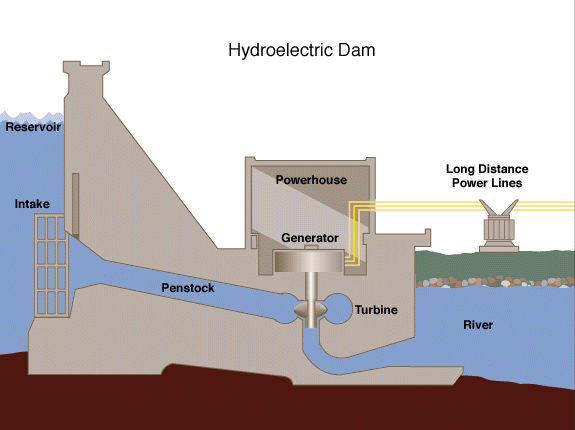
Image taken from https://kids.kiddle.co/Hydroelectricity#Run-of-the-river
An alternative approach is employed at "run-of-the-river" hydropower stations, which have small or no reservoir capacity. In such stations, only the water coming from upstream is available to generate electricity and any oversupply passes without being utilised. This is a big disadvantage and therefore a constant supply of water from a lake or existing reservoir is preferred!
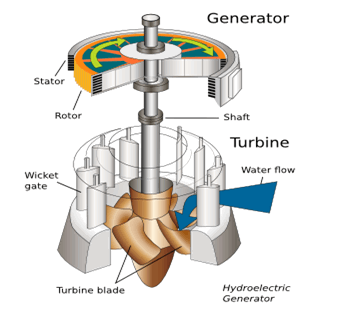
Image taken from: https://kids.kiddle.co/Hydroelectricity#Run-of-the-river
What are the advantages of hydropower?
Generation of electricity using water is more environmentally-friendly than burning fossil duels like oil or coal. It is renewable, powerful, safe and produces no waste.
It is also very efficient. This is useful at times and in places where the electricity demand is high. Water which is stored in a reservoir can be released to generate energy whenever required. This makes hydropower more easily controlled than solar or wind energy, which are dependent on the weather.
Can you think of any disadvantages?
Similarly to other power sources, there are some drawbacks to hydropower. Some obvious disadvantages include the loss of land and the damage to the local ecosystem where the dam and reservoir are created. This might even result in people having to relocate and leave their homes! Another disadvantage is the emission of the greenhouse gas methane generated by the reservoirs.
Watch the following youtube video to learn more about hydropower:
Let's experiment with hydropower!
Can you use hydropower to lift an object?
What you will need:
- 2-litre plastic water/soda bottle
- Ruler
- Marker
- Craft knife (have an adult help you use it)
- Scissors
- 2 corks
- 1 wooden barbeque skewer
- Sewing thread (16 inches)
- Small objects to lift (small fishing sinker, an eraser)
- Sink
- Duct Tape
- Large Funnel
- Paper clips
Procedure:
1. Using your marker and ruler, measure and mark a few dots 6 cm up from the bottom of the bottle. Connect your dots and have an adult help you cut off the bottom using the craft knife.
2. Measure an 8 cm section from the cut part of the bottle. Cut out this section so that you have a cylindrical section of plastic.
3. Cut four 2 cm-wide strips from the 8 cm section with your scissors. Cut these strips in half so you are left with 8 curved strips that measure 4 cm by 2 cm.
4. Draw 8 evenly spaced lines lengthwise on the cork, and make slits along each line with your craft knife (please, ask adult to help you with this). Making sure that the plastic pieces all curve in the same direction, slide each 4 cm by 2 cm plastic piece into its own slit.
5. Unfold two paperclips and flex one end of each to create a small loop. These paperclips will act as supports for the water wheel’s axle.
6. Affix your supports on opposite sides of your plastic funnel using your duct tape.
7. Cut the skewer in half and poke each half into one side of the wheel cork. Guide each end through a loop on your paper clip support. Make sure your paper clip’s loops are loose enough to allow the wheel to turn freely.
8. Insert one of the skewers into the other cork and tie thread tightly around it. Tie the loose end of the thread to a weight or other small household object.
9. Place your completed water wheel under a gentle stream of water in your sink. Slowly run water over the wheel so that the plastic pieces on the cork catch the falling water and turn it into mechanical energy.
What happened? Did you manage to generate enough hydropower to lift the object up?
The activity was retrieved from https://www.education.com/science-fair/article/water-produce-energy/
Blog post by Konstantinos